Search Engine Marketing
SEM’s meaning can often be fluid, depending on which marketer you are talking to. However, search engine marketing is widely agreed to be a mixture of both organic & paid search tactics to increase traffic, and, in turn, sales/leads.

Online businesses often employ search engine marketing to reach customers at a key point in the buying cycle when they are most likely to complete a transaction. To do this, business owners need to be aware of how their potential customers are searching for products & services.
Sounds like a lot of guesswork, right?
Fortunately for us, the guesswork has been almost completely eliminated from modern marketing through keyword research.
SEM Foundations – Keyword Research
Correct keyword research procedures should make up the cornerstone of any online marketing campaign, providing data and insight into how potential customers are using search to discover and purchase products or services.
Any digital marketing campaign that doesn’t perform due diligence in their keyword research is doomed to failure.
Keywords inform your marketing strategy.
What is a keyword?
If you have been marketing online for any amount of time, you will already be aware of keywords. However, if you are brand new to digital marketing, a keyword can be defined as a search query with volume.
Search queries are questions or search requests that have been used within a search engine, and the volume is how many times that query has been searched for each month.
Marketers can use this information to create on-page commercial and informational content & copy to boost organic traffic while leveraging the correct relevant keywords in paid ad campaigns.
Using keywords to inform your marketing isn’t always about trying to compete with the competition directly, it is also about finding gaps within your niche that your competition has failed to recognize and capitalize on the opportunity.
Types of Keyword
Not all keywords are equal; many digital marketers place too much focus on keyword volume and keyword difficulty (how hard it will be for you to compete within the SERP for that keyword.) Different keyword research tools use different metrics to determine this score.
It is all too common, especially for new marketers, to neglect the intent behind the keyword.
Keywords are typically split into informational keywords (keywords seeking information) and keywords with buyer intent. Depending on your strategy, you may only need to focus on one or the other; however, you will likely be targeting both.
Search queries with informational intent are useful for digital content marketing and SEO strategies by providing answers to the user’s search query. Typically, this will take the form of blog posts covering guides, how-tos, and generally satisfying the user intent.
If a user is making queries with clear buyer intent, we can leverage this information to place our products, services, and sales funnel pages in front of them, winning the conversion and making the sale.
Depending on your niche or industry, these are the types of keyword you should be looking for:
Service & Product Keywords
Typically, at the beginning of the buying cycle, potential customers may not be explicitly looking for a specific, branded product. Instead, they are likely to be aware of what broad service or product will provide the solution to their problem.
Marketing is more than just placing your products in the right place – you need to convince the customer that you have the solution to meet their needs.
Examples of service keywords users might search for:
‘Roofers near me’
‘Plumbers [City]’
‘Lawyers in [City]’
Etc.
Product keywords for someone currently redecorating their house may include:
‘Wooden furniture’
‘Modern furniture’
‘Dining room set’
‘Bedroom furniture’
Etc.
As you can see, non-branded service & product keywords are typically generic and can be as specific or broad as required. However, the more specific the keyword, the higher the likelihood that there is buyer intent behind the search.
For instance;
If a user searches for ‘Oak four poster bed’ instead of ‘Bedroom furniture,’ they are likely out of the investigation phase in the buying cycle as they have already made their choice and want a four poster bed made from oak.
It is now your job to get the click and convince them they should buy from you.
Feature Keywords
Feature keywords may look similar to product or service searches; however, the buyer intent is normally higher, as instead of focusing on broad terms, the user is looking for specific features.
For example, instead of searching for ‘Roofer near me,’ as I would if I was considering renovations to my roof. If my roof were damaged during severe adverse weather, in its place, I would search for – ‘Emergency roofer,’ or ‘24H roofer.’
Such searches focus on the service features, ‘emergency’ & ‘24H,’ promoting urgency and indicating increased buyer intent.
When doing your keyword research, you should be thinking about what unique features, services, or products you offer to the customer.
Particularly if they address specific issues your audience is at a high likelihood of experiencing.
Commonly, feature keywords can be forgot about or missed by your competitors, leaving a gap in the market for you to take advantage of.
Other examples include:
‘Divorce Lawyer’
‘Interest free credit card’
‘Budget [Service or Product]’
Etc.
Buyer Intent Keywords

High-intent keywords let us know that a potential customer is close to the end of the buying cycle and ready to make a transaction. As marketers, we should place a priority on keywords with high buyer intent to boost our chances of capturing leads and sales from users who are motivated to buy.
High-intent keywords come in many guises, some may seem investigatory, or feature focused. Still, they are usually used to help the customer convince themselves they are making the right decision, searches such as:
‘Best x’
‘Best x under $xxx’
‘Best x for y’
Etc.
Remember, high-intent keywords are highly competitive, as that’s where the money is made. To compete effectively, you will need a robust search engine marketing strategy, leveraging paid ads in conjunction with organic search to have any chance of success.
Competitor Keyword Analyses
An essential facet of keyword research is to perform in-depth and thorough analyses of your competition.
Not only will it allow you to discover the keywords they are currently targeting, and what they are having the most success with, but it will reveal gaps in their strategy that you can take advantage of.
The approach to competitor research is different for both organic and paid search. I will cover each in more detail further in the post.
How to do Keyword Research
To effectively research keywords, you’re going to need access to keyword research tools, and I have a post covering all the best keyword research tools that you can read here.
However, I will list one or two of my favorites here for you to check out in the meantime:
aHrefs
URL: www.ahrefs.com
Cost: From $99 monthly subscription
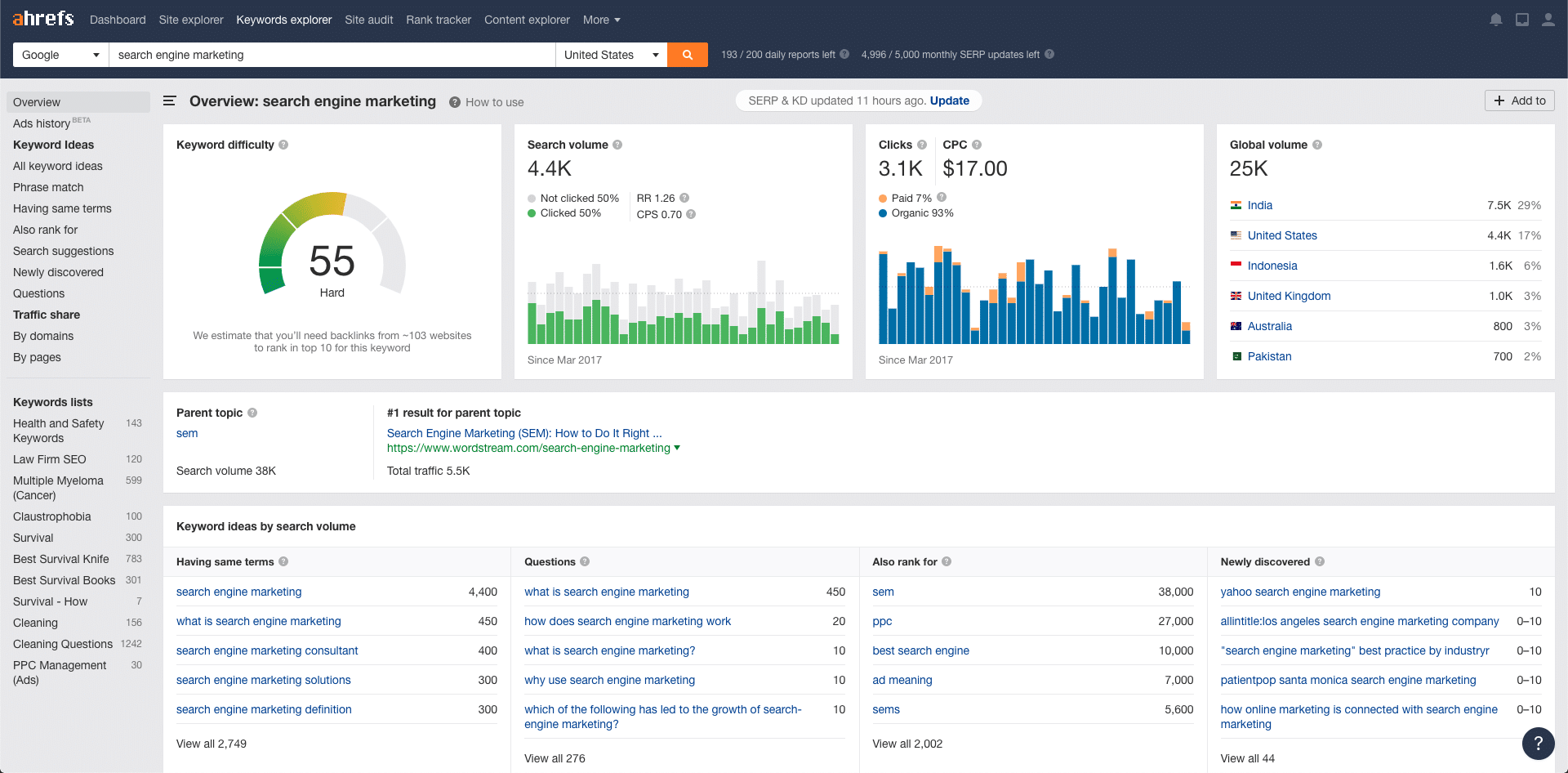
aHref’s is an industry-standard all-in-one suite of SEO tools, allowing users to track their keyword rankings, examine backlink profiles in detail, and see how you stack up next to the competition.
However, one of the best features is aHrefs Keyword Explorer, providing users with accurate keyword data, keyword suggestions, and competitor keyword analyses. If you were to only use one tool for digital marketing, aHrefs would be it.
Ubersuggest
URL: www.ubersuggest.io
Cost: $8 monthly subscription
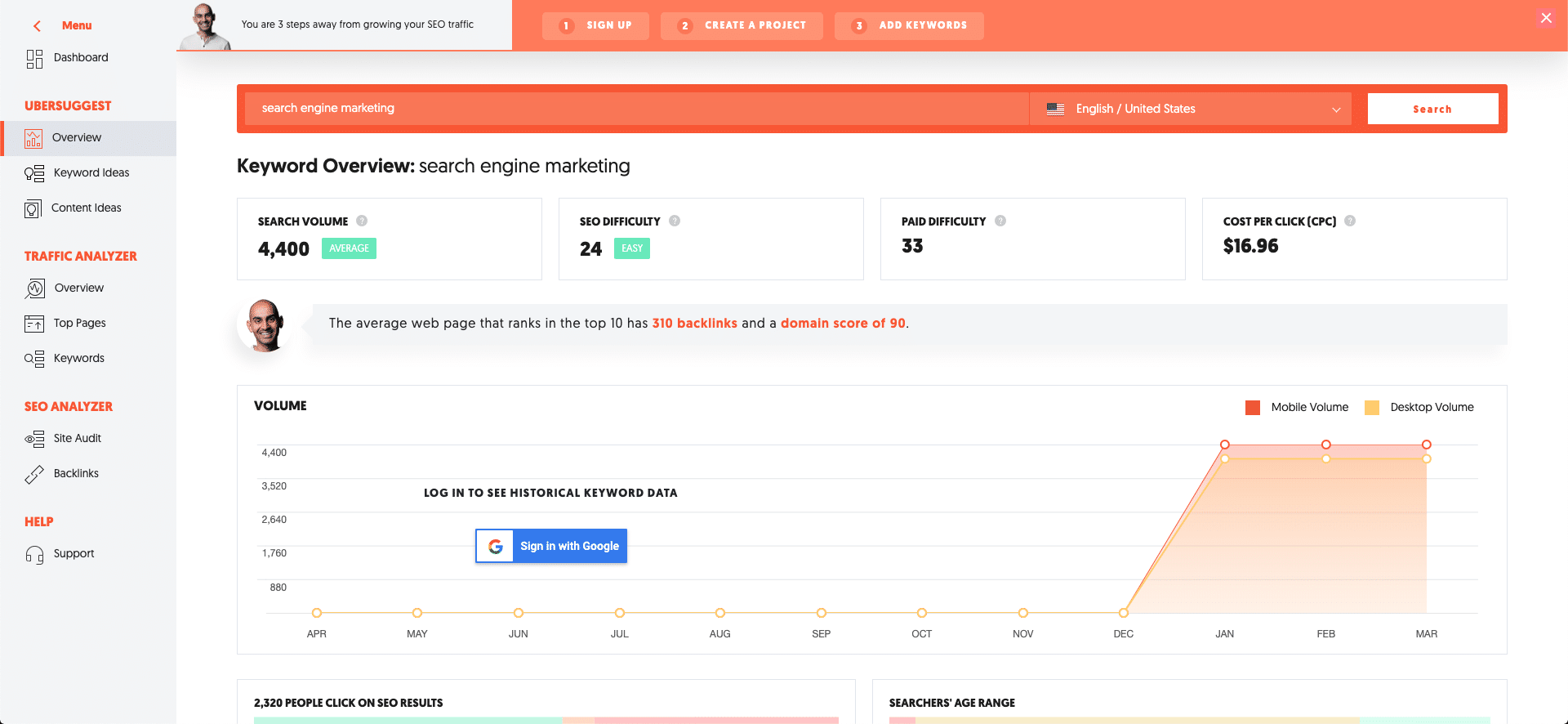
Until recently, Ubersuggest was entirely free; however, even at $8 a month, this tool is an absolute steal. Similar to aHrefs, Ubersuggest Is an across-the-board SEO suite capable of keyword research, rank tracking, and competitor analyses.
Not only that, but Ubersuggest will audit your site for SEO errors so you can stay aligned with best practices for technical SEO.
Ubersuggest shines when you utilize its keyword suggestion function, making it simple to find hundreds of relevant buyer intent keywords in minutes.
SEO & Organic Search
SEO, search engine optimization, organic search, or inbound marketing are all names that are often interchanged when talking about search marketing.
SEO specifically relates to optimizing on-page and off-page aspects of your website to inform search engine algorithms that your site is a trusted source of information, and deserves to appear in search results.

SEO uses two distinct sides of the same coin – on-site and off-site.
Each commands its own diverse set of best practices, and strategies that can be implemented to increase visibility within the SERPs.
Below, I will cover several aspects of both on-page & off-page SEO – including standard best practices and tactics used.
On Page SEO
On-page SEO is anything within your control that is contained within the content of your website. Google, and other search engines, consider several elements of on-page content as ranking factors.
Keyword density, page load speed, and internal linking, among others, are all considered when ranking your site. Also of great importance is the quality of the content you are publishing.
Search engine algorithms are becoming ever more complex, and with NLP and machine learning becoming commonplace, soon only the best content will be able to compete. As it stands, you need to deliver on user search intent, succinctly meeting user expectations without adding additional fluff.
Throughout the rest of this section, I will list some on-page SEO best practices that you should be following, as well as content types you need to publish and why.
SEO Best Practices
These are 9 of my favorite tips for anyone starting their SEO and digital marketing journey, by following these on-page SEO tips you will have created a solid foundation for future growth.
1) Use Your ‘Focus Keyword’ Early

When you are creating your on-page content, keyword density needs to be a considered factor throughout – it is a major indicator to Google regarding the subject matter of your content.
What you may not be aware of, however, is that positioning of your keywords is important also.
A general rule of thumb is to have your focus keyword appear within the first 10% of your content – some SEO’s stand by placing focus keywords within the first 100 words.
A focus keyword is the primary search term you are targeting.
Often, your focus keyword will be the title of your post, as Googles algorithm weighs terms that appear sooner more heavily when calculating ranking factors.
2) Avoid Duplicate Content
Creating duplicate content across your site can be disastrous; Google themselves have even stated that we should avoid:
“Having duplicate or near-duplicate versions of your content across your site.”
This rule applies to anywhere that you may create copy or content within your site including:
Meta Descriptions
Title Tags
Landing Pages
Blog Posts
Image Alt Text
Category Pages
Product Pages
It is also worth noting that creating on-page content on very similar topics, albeit with slightly different focus keywords, is inferior practice – leading to ‘cannibalization.’
Cannibalisation leads to traffic being shared among several pages for the same keyword. This can have adverse effects if, for instance, one page has commercial intent for sales, and the other is informational.
If the informational content is stealing traffic from your money pages, you are likely losing out on sales and revenue.
For eCommerce sites with hundreds or thousands of product pages, it is a hard task to create unique content for products that may only vary by color.
Red Baseball Cap, Blue Baseball Cap, Yellow Baseball Cap - and so on.
This is when the canonical tag comes into play, allowing you to distinguish between unique and duplicate pages.
3) Title Tags

SEO specialists have known for a long time that title tags play a significant role when determining your SERP positioning.
Google has publicly said: “…it is important to use high-quality titles on your web pages.”
For on-page SEO purposes, this means ‘front-loading’ our keyword – starting our title tags with the focus keyword.
Google, and other search engines, use your title tag to determine relevancy – close attention is paid to words and phrases that appear early.
However, it is worth noting that this shouldn’t be forced and unnatural; your title tag also needs to be relevant for users.
Unnatural looking title tags may reduce traffic to that page; instead, you should focus on placing your target keyword within the title tag as soon as it is natural.
PROTIP: make sure you limit keywords to one per title tag, ‘keyword stuffing’ has a detrimental effect on your ranking.
Years ago, it was common practice to place as many keywords as possible throughout the content as part of your on-page optimization; however, Google caught on to this strategy and now penalizes webmasters for using this tactic.
4) Loading Speed
Loading speed might seem like more of a user experience (UX) issue, but Google themselves have mentioned it as having a large impact on your ranking potential.
Therefore, having a site that loads rapidly is advantageous, not only as a ranking factor, but slow load times can affect other metrics, leading to a downturn in positioning.
If a site takes too long to load, there is a high chance that the user will return to the SERPs to find another source; this will increase your bounce rate – another ranking factor Google has implemented within their algorithm.
PageSpeed Insights is an excellent tool that will analyze your pages, providing loading time metrics that let you know how well your site is performing. And since the data comes straight from Google, you know it is worth actioning on.
Not only that, but PageSpeed provides users with an in-depth, detailed breakdown of the issues and how to rectify them.
So, what practical steps can you take to improve load speed immediately?
Compress Images – Compressing the file size of your on-page images is a quick win anyone can achieve with minimal effort. Using a tool like Kraken.io streamlines this process for inexperienced or new SEOs and digital marketers.
Use a Lighter WP Theme – If you are using WordPress as your CMS, you may be using a theme that suffers from code bloat, negatively affecting the loading time of your site.
Lazy Loading – Having your images load only as required, i.e., as the user scrolls your page, images load only as they are needed. Lazy loading can boost load speed by up to 50%; however, it should be worth noting that there is potential to affect UX, and you will need to test results to make the correct judgment.
Use a Content Delivery Network – CDN’s provide images and media to your users via server’s that are closer to their location, resulting in decreased load times.
5) Google Search Console

In our current year, if you aren’t using GSC, then you are missing out on valuable information that you could be leveraging to get a leg up on your competitors.
Google Search Console provides you with a dashboard, informing you of how well your site is currently performing in the SERPs.
There are many features to be found within the Search Console; however, I recommend only focusing on the below three reports consistently.
Performance – Performance provides impression and click data for your site, letting you know how many people have seen your website and how many have clicked through.
The exact traffic source keywords are also featured, letting you know what people are searching to find you, and where you rank.
The best way to use this information is that if clicks/impressions are consistently going up, you’re doing ok. If not, it might be time to change tactics.
Coverage – Coverage lets you know which of your pages Google has indexed, and whether or not there are any issues with their bots crawling your pages.
Any warnings or errors found here should be fixed ASAP; if your page isn’t indexed, then it will never appear in organic search.
The good thing is, if your page can’t be indexed, GSC will usually tell you why.
Enhancements – Pay close attention to ‘Mobile Usability,’ Google now uses mobile-first indexing. So, it should be a priority for you to ensure your site is mobile friendly.
6) Images
SEO for images is about more than just ranking on-page images within Google images tab, and it is now possible for pages to rank for alt text content in organic search.
This means that not only do your image filenames need to be descriptive of the image content, but the alt text should be as descriptive as possible.
It only takes a couple of seconds to write a line of alt text for your images, yet it can have a profound effect on your SERP visibility.
7) Internal Linking

A robust internal linking strategy is another quick win that is easy to implement and plan for in the future.
Essentially, internal linking is linking from one page on your site to another.
PROTIP: Don’t get carried away and start linking randomly between your pages; there is a correct method to follow. However, random internal linking is better than zero internal linking at all.
To get the most from your internal linking structure, you should follow these tips:
Keywords in Your Anchor Text – When Google is crawling your site, anchor text is used to understand the relevancy of any links they find. Using the focus keyword of the page you’re linking to is ideal, but it must appear natural and unforced.
Share Authority Between Pages – If you have pages that are doing well within the SERPs, that means they hold a lot of authority. It is good practice to link from your more authoritative pages to underperforming pages to share some authority or ‘link juice’ with them.
This can provide you with some quick wins when linking internally to a page that you want to start performing better.
The easiest way to keep on top of internal linking without it becoming too convoluted is to link from older pages to your newer content. New pages tend to have lower authority than older, more established pages.
8) UX (User Experience)
General UX may seem to be a design issue, but it can have both positive & negative effects if the user experience is poor. If your site is poorly designed, features invasive pop-up ads or banners, takes too long to load, or is full of broken links – people are going to return to the SERPs to seek other options.
This is going to decrease dwell-time and increase your bounce rate, telling the search engine that the user hasn’t found what they were looking for.
Google & other search engines see this and assume that your site isn’t relevant to the user’s search intent and drops you lower within the rankings – even if the content is excellent.
9) Publish Quality Content

Anyone who has blogged or been involved in digital marketing for a short while will undoubtedly have heard that ‘content is king.’
This concept hasn’t changed, if anything, more time and effort is being placed into quality content production than ever before.
By publishing high-quality, data-driven, relatable content that contains unique insights, you cement yourself as an authority within your niche or industry – building trust with your audience.
Creating quality content takes time, effort, and money – not necessarily all three at once. Still, if you are an affiliate marketer working as a one-man-band, you are likely doing everything yourself or outsourcing content production at cost.
The topic of content creation leads me to the next section in on-page SEO, types of content you need to create to engage with your audience.
Types of Content You Should Be Making

On-page SEO for search engine marketing requires you to produce a varied array of content assets that are then leveraged for different purposes.
Commercial content (commercial blogs & landing pages) are used to generate revenue through various means and strategies. While Informational assets are used to build site authority through backlinks and social shares
Blog Posts
The majority of your on-site content/copy is going to be through blog posts. There are two key types of posts you will need to create, and both have distinct functions.
Commercial
Commercial blog posts are used to target high-intent money keywords to sell products & services to potential customers. Commercial blog posts will often take the form of product reviews and recommendations.
Using your blog to compare products, create round-up reviews of the best products, or review them separately are some of the more popular ways a blog is used to sell products to users.
This is a common tactic used among affiliate marketers, using their platform to insert affiliate links into their review content.
However, since commercial content targets high-intent keywords, it can be hard to beat out the competition and rank within the SERPs for the same terms.
This is why you need to become an authority within your niche or industry.
Informational
Informational content is used as part of our on-page SEO strategy to deliver high-quality, relevant, sought-after information within the marketplace.
Informational content goes hand in hand with off-page SEO tactics like link building (more on that shortly) and helps to build our site authority.
By ranking for informational content, we can funnel our page authority to our commercial pages, increasing not only their authority – but the overall authority of our site.
Content that contains guides, how-tos, and FAQ’s are all considered good starting points – anything that answers questions and provides solutions.
Now, while those options are great, what we really want is for people to link back to us from their website, and while you can gain a significant number of backlinks from the above content types – there are two others that, in my experience, perform better.
Longform Content
Longform content is one of the best ways to develop your site authority. Going in-depth into a subject and providing a wealth of information for your readers that is above what your competitors offer can prove invaluable.
Creating longform content can be time-consuming, and may require specialist knowledge, but the return in site authority can be huge. You can also release longform content in chapters, taking the opportunity to have users opt-in to your email subscriber list so they can be informed when the next chapter is released.
The best longform content should be on a subject that will remain evergreen – meaning it always stays relevant. You can create longform content on fast-moving subjects, but you need to be willing to go back and update them regularly with industry or niche changes.
Brian Dean of Backlink.io is a master of creating longform content and has grown into one of the most prominent authorities within his niche.
Case Studies

Case studies provide knowledge and actionable information to your audience through in-depth research & testing of scenarios & working practices. Not only do they establish your authority as a thought leader within your marketplace, the information contained within makes for a highly shareable, unique asset.
And because the data provided is sourced from your own testing and methodology, it is tough for your competitors to steal the information without risking their reputation.
A well written, relevant case study is one of the best ways to source backlinks from people within your industry, citing the case study data within their blog content.
However, case studies need to be more than just a data report; they should be personably written and contain the insights you have gained from the exercise. Show the audience how you did it, why you did it, and what benefit they will get from replicating your results within their own work.
Landing Pages
Landing pages are standalone web pages, created for specific marketing & advertising campaigns. When a user clicks a link within a paid ad featured in the SERPs, from social ad platforms, or through e-mail marketing, they are redirected and ‘land’ on these pages.
Landing pages are designed with one function in mind, convincing the user to complete the desired action. Whether that be to buy a product, sign up for a service, or join an email subscriber list.
Because landing pages are hyper-focused towards a single goal, they are one of the best options for increasing conversion rates while keeping CPA (cost per acquisition) down.
You have undoubtedly seen landing pages before when looking for products and services yourself, and they come in many different variations. Still, the truth is, there are only two real landing page archetypes.
Lead generation landing pages & clickthrough landing pages.
Lead gen capture pages should feature some type of sign up form as their primary CTA (call-to-action) and are used to collect user data – typically, e-mails, names, and phone numbers.
Lead generation like this is often incentivized with eBooks or money off coupons, and the information is used for retargeting the user with further marketing opportunities.
Clickthrough landing pages are often used to sell products and subscriptions, using a redirect CTA button to take the user to the product page, or straight into the checkout flow.
Landing pages are a great addition to any marketing funnel, as there are many ways to drive traffic directly to the page.
By using a mixture of paid search, including paid social, email campaigning, and organic search, it is possible to drive thousands of clicks to your landing pages for minimal investment.
Increasing not only your conversion rate but overall ROI (return on investment.)
Videos

Video marketing has been used since the widespread introduction of televisual services within our homes. Yet, it is often never considered as part of a content marketing strategy.
Yet, did you know that including video within your marketing strategy can boost conversions by up to 80%?With 64% of consumers making a transaction after watching videos on social.
Not only that, but sites that use video within their content marketing strategies are more likely to reach the first page on Google, 53 times more likely in fact.
Video is highly engaging, and users are becoming accustomed to consuming video content over text – marking a significant change in the way people need to be marketed to.
Video is an excellent addition to both informational & commercial content, and 4x as many customers claim they would rather watch a product video than read about it.
What does this mean for content marketers?
It means that video content is becoming increasingly necessary as part of our on-page strategy and, conveniently, video can be repurposed for paid ads on social platforms – and, in some cases, monetized through services like YouTube.
The same principles that apply to written informational and commercial posts apply to video marketing. Content must be of high quality and offer value to the user.
CTA’s should be used within your video content & descriptions to direct your audience towards your landing pages, getting them started within the sales funnel.
Custom Images & Infographics
Infographics are highly shareable assets that allow you to distill a lot of information down into an easily digestible medium for the user. Often used to offer a visual representation of statistics and data analyses, infographics are a proven tool for promotion.
Good infographics (especially if they go viral,) will source you a significant number of backlinks without the level of time-investment needed to conduct a successful link building campaign (and can even form part of your overall strategy.)
Once an infographic has been shared several times, it should continue to generate backlinks and shares for you with little to no additional input – as long as the information remains relevant.
eBooks
Setting out to write an eBook can seem like a mammoth task, especially if you have never done it before. Yet, they often form a vital component within incentivized opt-in campaigns – offering the eBook in exchange for the user’s contact details.
If your eBook is well written, contains useful quality information, offers value, and remains evergreen, it can act as a successful lead magnet for years.
eBooks tend to convert better when they offer real, actionable insights for the users – rather than act as a platform intended solely to promote your brand.
Off-Page SEO
What is Off Page SEO?
Any action taken outside of the confine of your website, that has the potential to affect your SERP positioning, can be clarified as off-page SEO. Off-site SEO is based on optimizing for ranking factors that can be manipulated to improve search engine, and user, perception of a site’s trust, popularity, relevance, and authority.
Typically, these factors are boosted by reputable sources linking back to your on-page content. The more authoritative the source of the backlink, the more likely it is that Google will see your site more favorably.
Backlinks are essentially upvotes for Googles algorithm, letting them know that you are a well trusted or popular source of information.
It should be known that while curating a significant and diverse backlink profile is the heart of off-site SEO, social signals and other non-link related options do exist.
Off-page SEO success is directly linked to your on-page efforts, as I said before, they are two sides of the same coin; if your on-page SEO isn’t up to scratch, your off-page SEO will fail.
Link Building for Off-Page SEO
Out of an estimated 200+ ranking factors used by Googles algorithm when ranking a site, the backlink profile is considered to be #1 – although that might be about to change.
Even if backlinks are becoming less relevant, they will undoubtedly remain one of the top factors within SERP positioning and shouldn’t be ignored.
A considerable level of time investment is made every day by marketers looking to build a noteworthy backlink profile to boost their, or their clients, online profile & visibility.
For gaining organic traffic, having an effective & robust link building strategy at the forefront of your inbound marketing campaign is vital. However, for link building to remain successful, you must have a quality, linkable asset at your disposal.
Other webmasters, bloggers, or marketers are unlikely to link to poor content, as it disrupts the user experience quality on their site.
Link Quality
Not every backlink is positive; links from questionable sources such as PBN’s (personal blog networks) are known to have a negative effect, with Google handing out manual penalties to anyone caught manipulating their backlink profile in such a way.
Links from large sites that carry a significant level of trust and authority, especially if they are within the same niche/industry (relevance is essential,) will weigh heavily in your favor.
However, organic links gained from small, low authority sites are still useful, and it is estimated that the average authority of your overall backlink profile is more important than the individual links.
The Upper Ranks have a great post on the perfect backlink profile that you can read here, where they assess the backlink profile of several websites to see what makes them successful.
Link Building Strategies
Numerous link building strategies have been developed over the years; however, most are variations on these four steps.
- Create a high-quality, informative, linkable asset as part of your on-page SEO strategy.
- Prospect (search for or seek out) potential link targets – these are relevant websites that may be interested in sharing your content with their audience.
- Outreach via e-mail to each prospect with your content
- Get link
That’s it, albeit broken down to its most straightforward aspects. Yet, most link building strategies follow the same progression, with the key difference being how the prospects are found.
Occasionally, you will create content after a backlink has been agreed upon with the prospect, typically in the form of guest posting.
For a content marketer to successfully conduct link building campaigns, they need to be highly organized; large link building campaigns can deal with hundreds or even thousands of e-mail threads at once. Mail management tools are crucial to realizing link building success – popular options include MailChimp, EmailOctopus, and MailShake.
So, let’s take a look at some of the most popular strategies being used by digital marketers around the world today to build desirable backlink profiles for themselves and their clients.
Guest Posting/Sponsored Posts
Guest posts have remained one of the most popular link building strategies among bloggers and content marketers over the last decade, and for good reason.
The principle behind guest posting is simple; you contact other webmasters/bloggers asking if you can craft content they can use on their website or blog in return for a link placement.
Prospecting – finding placements for guest posts – remains difficult for some, but I have found the easiest way is to use advanced Google search operators in conjunction with relevant keywords.
Search operators are commands used within the search engine to refine your search results.
aHrefs have provided a post on how this is done here.
While prospecting for guest posts can prove time-consuming, it is possible to find several hundred prospects that you can outreach to. You must keep in mind, however, that not only do you need to perform the prospecting & outreach, but the content will need to be written once a prospect agrees on a guest post placement.
This time-sink must be factored into your workflow.
Still, freelance writers found on Fiverr & other services can provide the required content for a relatively low investment.
About 60% of the time, the prospect you have reached out to will request money in exchange for a post - this is known as a sponsored post.
Usually, you can haggle to bring the cost down; it is often worth paying for sponsored posts, and you will have to decide on a case by case basis whether it is worth the price. To sweeten the deal, the prospect will often offer to create the content for you.
Don’t limit yourself to only prospecting to bloggers and sites that advertise guest posting services, if you are confident in the level of content you produce – you can outreach to large authoritative sites that don’t necessarily offer guest posting opportunities.
More often than not, they will turn you down, but occasionally they will take you up on your offer, especially if you have noticed a content gap on their site and have offered to create it for them.
A single link from a relevant, authoritative site can have profound effects on your rankings.
Link Hi-Jack

Link hi-jacking is used to steal links from your competitors; however, you need two things before you can act on a link building strategy like this.
Firstly, you need to have high-quality linkable assets or be able to create them as needed. Secondly, you also need access to a backlink analysis tool such as aHrefs, Moz, or Ubersuggest.
Most of these tools offer similar functionality, but for this blog, I will assume that we are using aHrefs. However, the principle still stands regardless of which tool you are using.
By the time it comes to staging link building campaigns, you should have already identified the main competitors within your niche/industry.
Place the URL of your main competitor into aHrefs site explorer, and filter to view their pages as ‘best by links,’ next you should sort by referring domains.
You will now be presented with a list of your competitor’s most linked-to site pages, which allows you to extract a list of backlink sources – these are now your campaign prospects.
Next, if you already have comparable content that is of a higher quality than theirs, you can outreach to each prospect and offer your content as a replacement source of information for their readers. Swapping your competitor’s link to one that points to your chosen on-site content.
You can also create content specifically for this purpose, identifying posts on your competitors’ site that you believe you can create a superior asset against.
This link building technique is best used by intermediate marketers, and the level of success is more determinate on the quality of content you produce than other link building methods.
Broken Link Building
The internet is very much similar to an extensive collection of living organisms, in that old sites are continually dying off to make room for new sites. When a website, or single page, ‘dies,’ or is removed – any links pointing to that page will result in a 404 error.
This means that if we can find pages on our competitors’ websites that are being linked to, yet no longer exist, we can offer our content as a replacement.
Again, using aHrefs, we can scrape through our competitor’s pages and filter using the ‘HTTP Code’ dropdown box for 404 errors. We can then export all the referring domains that are currently linking to each broken page.
We now have a list of prospects we can reach out to with comparable content or create the material before we start outreach. Most webmasters will be happy to exchange the broken link for yours, as not only have you helped improve the UX for their users, you have provided an easy solution to the problem.
An added bonus of broken link building is it can lead to good relationships with the prospect you have outreached to, boosting your organic backlinks going forward.
Link Vendors

If you don’t have the time to scale your link building campaigns to an acceptable level but have access to a budget – it might be worth considering a link vendor.
Link vendors are typically utilized by content marketers to score some quick wins and shouldn’t be your primary link building strategy if you are thinking long term.
Link vendors generally offer one of two services – they will conduct prospecting and outreach on your behalf, or they will have access to a network of blogs they can use to point links in your direction.
However, there is always the danger of having your site spammed with low quality, spammy PBN links resulting in manual penalties from Google. You must remain vigilant when buying links, making sure you are tracking them correctly – disavowing any that may have adverse effects on your rankings.
However, using PBN links to point at domains that are already linking to you, boosting their authority, which then cascades down to you, is a common tactic known as tiered linking.
If you have someone conduct prospecting & outreach on your behalf, it is common that they will have established relationships with high-authority sites within your niche. If this is the case, these links are worth the cost and are generally natural-looking and safe.
Paid Search
While a good on & off-page SEO strategy will boost your organic traffic, driving users to your site without an inherent monetary cost associated. Paid search, PPC ads, or paid ads, are used by marketers to buy traffic from the SERPs.
Paid search is highly competitive, with an estimated yearly expenditure of $135billion worldwide throughout 2019.
Because so many businesses and marketers are competing to appear at the top of the SERPs, it is vital to employ a measured & well-thought-out paid ad strategy to remain competitive.

Alongside our keyword research from earlier, for paid search to be successful, we need to conduct in-depth competitor analyses.
Competitor Keyword Research
Knowing which keywords your competitor’s target is useful, as not only does it let you know which keywords you should also be targeting, but it can provide some insight into the marketing strategies they are using.
By analysing data from competitors, it is possible to find gaps in their marketing campaigns where you can operate with a lower level of competition – improving your overall performance.
SpyFu is a popular tool used by digital marketers to find out which keywords your competition is after, how much they pay per click, the SERPs they appear in & which position they hold. Spyfu even allows us to see the entire ad history of our competition – letting us know how their strategy has evolved over time.
When you are analyzing your competition, you want to find the high-intent, high-value keywords that are currently driving a lot of clicks. If you have the budget to outbid your competition & reach the number 1 spot, you can gain a significant advantage over them.
Essentially paying to have highly relevant, targeted traffic that will have otherwise landed on their site reach you instead.
Google Keyword Planner
After you have done your due diligence and performed in-depth, thorough keyword research – including competitor research, you should have an extensive list of terms you can potentially target.
Now it is time to use Google’s Keyword Planner to make final adjustments to our list, first by expanding it, then by removing unnecessary keywords.
Firstly, you need to enter the terms that you think are most relevant to your potential customers, using terms from the keyword research you have already done. Next, select the most applicable matches that are returned and add them to your list.
When you are selecting matches from Keyword Planner, you need to have set metrics in mind that correlate to not only your goals but your budget too. If the traffic for a keyword is too low, or the CPC too high to justify against your budget, you should abandon those keywords.
That isn’t to say you can’t keep a list of keywords you want to target in the future as your business, and in turn, your budget grows. For now, it is best to operate within your means to avoid financial losses.
Now that you have taken all these steps, you will be left with your final keyword list, curated from comprehensive keyword research and competitor analyses. You can potentially be left with thousands of terms on your list – it’s time to shorten that list.
Firstly, you need to upload your keyword research list into Googles search bar; while you can do this manually, it is much more efficient to upload it as a file.
Now it’s time to go through our list with a fine-tooth comb, looking at CPC, projected CTR, and search volume.
An ideal keyword is one that has high search volume, low CPC, and little competition – however, it is more than likely that those keywords won’t exist. When you are deciding which keywords to cut and which ones to keep, you have to consider relevancy first, then weigh your budget against the potential return on investment.
If you have the budget and think you can compete for expensive CPC, you should only target high-value services and products to ensure the best ROI.
Unfortunately, some elements of keyword research will come down to how well you know your industry, and how well you know your potential customers are searching online. This will require some experience on your part, but the more you run paid search, the better you get at it.
The last step is to sort your final keywords into ad groups, groups of related keywords a potential customer might be using to find products & services.
I.E., if you are running an ad targeting ‘Bedroom Furniture,’ you probably want to group ‘bed,’ ‘bedside table,’ ‘wardrobes,’ etc., into the same ad group.
You must always group your keywords by their relevancy and consider the search intent of the user.
You must continuously test and refine your ad strategy, optimizing for maximum conversions.
Split Testing for Paid Search

Split testing your PPC ads is vital for on-going performance and optimization. Since PPC campaigns often end up being one of the more expensive aspects of search engine marketing, you need to stay on top of conversions and ROI at all times.
Fortunately, split testing for PPC ads is more comfortable than A/B testing other aspects of your marketing campaigns – like CRO testing a landing page, for instance. However, that doesn’t mean any less care or attention should be paid into these tests.
What to Test
Split testing PPC ads is a much sleeker process than testing your web copy, landing pages, or email marketing – as there are really only four elements you can test:
- Ad Headline
- Ad Copy
- Ad Link
- Keywords the ad targets
The ad headline appears at the top of your ad as a link within the SERPs and should identify the offer. Ad headlines shouldn’t be convoluted, remaining short and to the point, more than five words can seem excessive.
The main keyword you are targeting should also feature within the ad headline and will appear in bold on Google. Your ad copy, or body text, can be thought of as the equivalent to a pages meta tag in organic search.
Your ad copy should inform the user of what they can expect and convince them they need to click your link.
Where the ad link points to is just as important as what is contained within the ad itself, preferably redirecting the user to a landing page/sales funnel or to a product page. You shouldn’t link directly to your homepage unless you only sell a single product, and the homepage acts as your landing page.
When considering focus keywords, you could target every keyword with a single ad. However, this can waste time and money. Instead, you need to focus on the keywords that will lead to higher conversion rates.
Focusing your budget on keyword combinations that convert well is better than attacking all keywords. When split testing focus keywords, you should not only focus on the individual search terms but the ad group combinations – some ads convert better depending on the search they are featured in.
Once you have figured out the potential variables you can test and have assigned values to them; you need to list all the possible combinations of tests you can run. For example, if there are two possible variations of ad link and two variations of ad headline, then you need to conduct four rounds of testing – AA, AB, BB, BA.
Remember, the more variables you want to test then the more tests you will need to run. Also, all your variables must make sense when combined in any combination; otherwise, you will need to eliminate the combinations that make no sense, are repetitive, or conflict.
Why You Should A/B Test
When you start split testing PPC ads, you need to have a goal in mind – what do you hope to gain from the testing process? Are you trying to build a highly targeted, relevant email subscriber that you can market to and convert in the future?
Or are you trying to gather immediate sales?
No matter what, you need to have a goal in mind so you can correctly optimize the campaign based on your test results.
Tracking Split Tests
![]()
When tracking PPC ads, the two most important metrics to monitor are clicks and conversions. The main focus should be on increasing both numbers, a high CTR combined with a significant conversion rate will provide the highest return on investment.
Depending on your budget, you should let tests run for at least a few days; however, it is preferable to gather data over weeks. The more data you have, the more accurate your optimizations can be.
You must also make sure you monitor ad positioning throughout testing. If you have bid too low for your keywords, you may find that your positioning shifts during testing. If there is too much fluctuation, the data can become unreliable as SERP positioning can affect the number of clicks you get.
Testing and optimizing is a never-ending process as variables within your ad can be infinitely altered. Some ads that were performing well for you two months ago may suddenly drop off for several reasons – seasonal changes, new products hitting the market, competing ads having more success.
A/B Testing Best Practices
When you are split testing pay per click ads, keep these four simple guidelines in mind when setting up your campaigns:
- Test all your ad variations concurrently to minimize time factors that can lead to unreliable data.
- Continually test and refine your ads.
- Test early, don’t sit on an ad campaign idea, set aside a small budget for testing ads immediately.
- Try not to rely on intuition too much; always refer to data before you make any decisions.
- Run your test campaigns for long enough to gather reliable data that you can act on. Too short and the testing may not provide an accurate representation of what is going on; the longer you test, the better the data is.
Ad Auctions

Often, it is thought that the marketing team with the largest budget will always win the top position within the SERPs. While a significantly large budget is always a bonus, how much you are willing to pay isn’t the only factor to influence ad position.
When you are running ads, before they are implemented, they go through what is known as the ‘ad auction.’ Each time a user runs a search via Google, the ad auction process starts.
To make sure you are competitive, you need to have identified the correct keywords and place a bid – the amount you are willing to spend per click through. If your selected keywords are aligned with the user’s search intent, you are entered into the ad auction.
Winning the Ad Auction
During the ad auction, several elements of your ad will be assessed as Google considers your ad position. If you are targeting keywords with low buyer intent, Google may never display them. After all, Google’s main priority is to provide users with a pleasant search experience, not bombard them with slightly relevant ads.
To do this, Google weighs your maximum bid per click against their ‘Quality Score,’ a metric they use to determine the overall quality of the ad from a user perspective.
This calculation results in an Ad Rank score for each of your ads; the ad with the highest Ad Rank calculation wins the top position.
To calculate Ad Rank, Google uses this formula:
Maximum CPC Bid x Quality Score = Ad Rank
Thoughts differ on which metric is more important, your maximum bid or quality score, but many top digital marketers consider quality score to be the most critical metric.
A higher Quality Score will allow you to bid less for each click, improving ROI, and maximizing your ad campaign revenue. Because of how Ad Rank is calculated, it is often possible for the ad with the lowest CPC bid to receive the highest ad position within the SERPs.
Google uses your ad relevancy, CTR, and landing/product page copy to determine your Quality Score. By improving each of these metrics, you can significantly boost the success of your PPC marketing.
Summary
Congratulations, you’ve made it to the end of this article, hopefully, wiser and more knowledgeable – ready to tackle your next search marketing campaign. I know there was a lot of information to get through, and I would suggest returning from time to time to refresh your familiarity with search engine marketing concepts.
Do you see much success with your search marketing? Let me know in the comments below, and feel free to share any hint and tips you have gathered over the years.
If you find yourself stuck with any topics discussed within this post, feel free to contact me, and I will do my best to answer all questions and cover any topics in future posts. You can also subscribe to my newsletter to receive free affiliate and digital marketing hints, tips, and strategies that I use every day.
Share the Love
If you found this post useful, please let others know about it by sharing it.



